
An offline python frontend for the QuadVisions Colab Notebook using tkinter. It offers basic options and interactively displays the generating image. So far PyramidVisions, FourierVisions and CLIP + CPPN are implemented. Image generation code: Jens Goldberg / Aransentin, Colab by Philipuss#4066. Now features Deep Daze and Big Sleep by lucidrains.
VisionsGUI was tested under Arch Linux and Windows 10 on a NVIDIA RTX 2070 Super. PyramidVisions, DirectVisions and FourierVisions require a card with at least 4GB of VRAM. The VRAM consumption of Deep Daze and Big Sleep is variable and mostly depends on the image size and depth. CLIP + CPPN requires more than 8GB. CPU only is currently not supported.
Python and CUDA are required, the remaining dependencies can be installed via pip. Using a virtual environment like venv is preferred to keep the required pip packages seperate from your existing pip packages.
- Install Python 3 and pip via
pacman -S python python-pip - Install the CUDA 11 toolkit via
pacman -S cuda - Install the pip requirements:
pip install -r requirements.txt
- Install Python 3
- Install the CUDA 11 toolkit
- Install the pip requirements:
pip.exe install -r requirements.txt
Python 3 should be available as a package for most distros but CUDA 11 might not be. In the latter case, an installer is available on NVIDIA’s site.
To start, run python visions-gui.py. An internet connection is only required when running a model for the first time. No connection is required after the model has been downloaded.

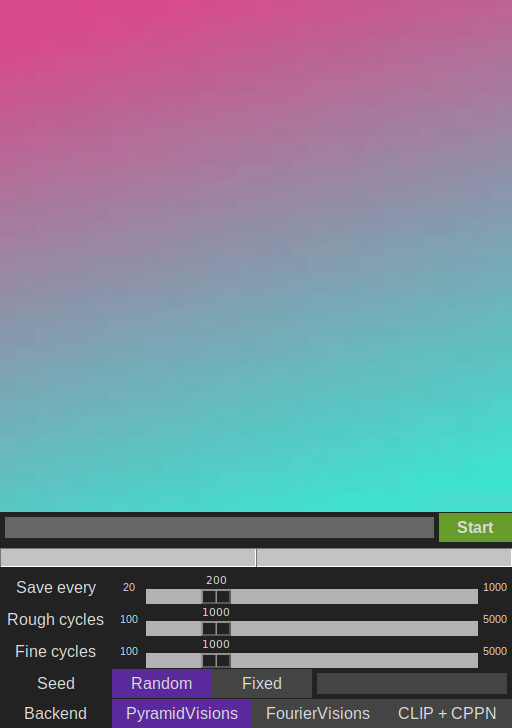
The gui is made up of multiple modules which offer feedback to the user and allow to change a handful of settings.
The image viewer displays the current progress of the image and is periodically updated during generation. The displayed images are also accessible in the images folder.
The prompt bar consists of a text field and a start / stop toggle button. A prompt is entered into the text field and the image will be generated as soon as the button is pressed. To stop, press the button again. The button also serves as the gui’s state:
| Color | State |
|---|---|
| Green | The model is ready and waiting to be started |
| Yellow | The model is currently generating an image |
| Red | An error occured |
The progress bar shows the progress of all stages.
The settings panel contains a few option for generating an image. Not all settings are available for all models:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Save every | Cycles completed before displaying and saving the next image. Lower values add more overhead. |
| Scale | Changes the size of the output image. |
| Rough cycles | Cycles during the first stage. |
| Fine cycles | Cycles during the second stage. |
| Seed | If a random or fixed seed is used. If fixed is selected, uses the the seed entered in the entry field to the right. |
| Backend | Which model to use |
VisionsGUI is expanded by adding model code and model settings to two python models without having to modify the existing classes. Have a look at the existing models and their settings definitions if you are unsure on how to set up the classes.
To work with the frontend, the model needs to save an image (currently .png support only) in the images/. folder.
Create your inference module in the models/. folder. Each class in your module needs to inherit ThreadedWorker from worker.thread.
Set the model up in the constructor and make sure to call the constructor of ThreadedWorker.
Place the inference code in method called function.
Define a list of integers named self.progress. The length of the list corresponds to the amount of different stages present in your model. The length only influences how many progress bars are show in the gui. At least on stage is required, otherwise the frontend wont stop refreshing the image and progress bar after the model finishes. Update the progress list after each iteration.
Create a new class inheriting from SettingsPanel, accepting a tkinter Frame and with the following structure:
- A constant called
backendpointing to your model class type. In the constructor: - Call the constructor of
SettingsPanelwith theFrame. - A list called
self.optionscontaining instances of tkinter objects. These objects need to implement thegetmethod which should return a dictionary of option names and their values. - Call
self.pack_options()Define a method calledapply_options(self, model)accepting an instance of your model. This function is called before the model is started: - Get the current settings set by the user with
self.get_settings(). This call returns a dictionary containing all option name and value pairs. If the same option name is used more than once, the dictionary will contain a list of values for that name. - Set your model settings from the options above.
- Add DirectVisions
- UI support for multiple text / weight pairs
- UI support for variable image sizes
- Compiled executables
 https://github.com/CoppaMan/visions-gui
https://github.com/CoppaMan/visions-gui